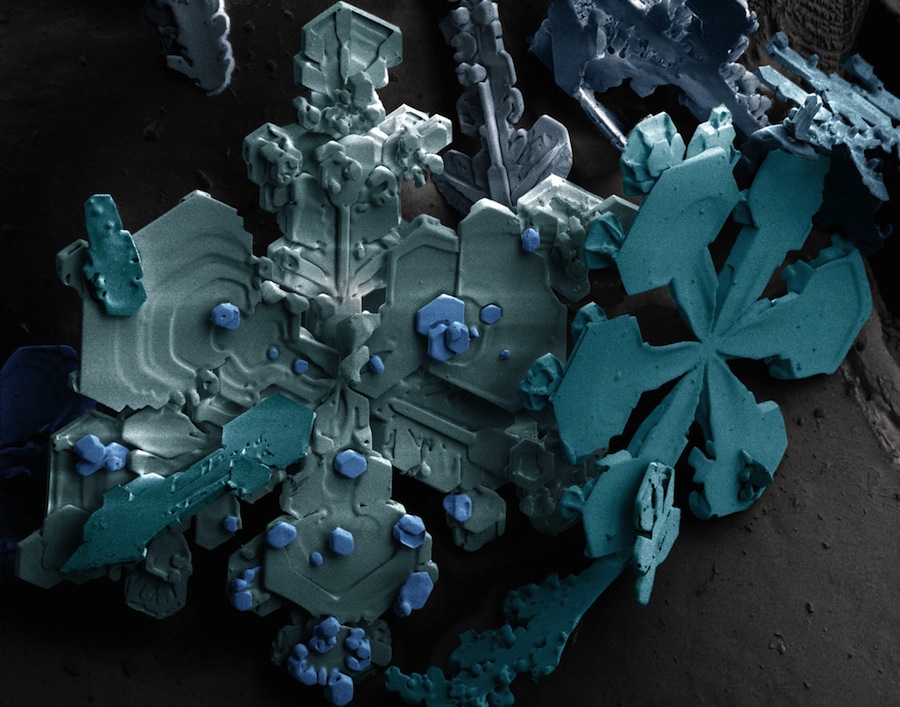
Snowflakes: ice crystals that fall directly from the sky as precipitation, usually grouped in bunches. Often these crystals are symmetrical.
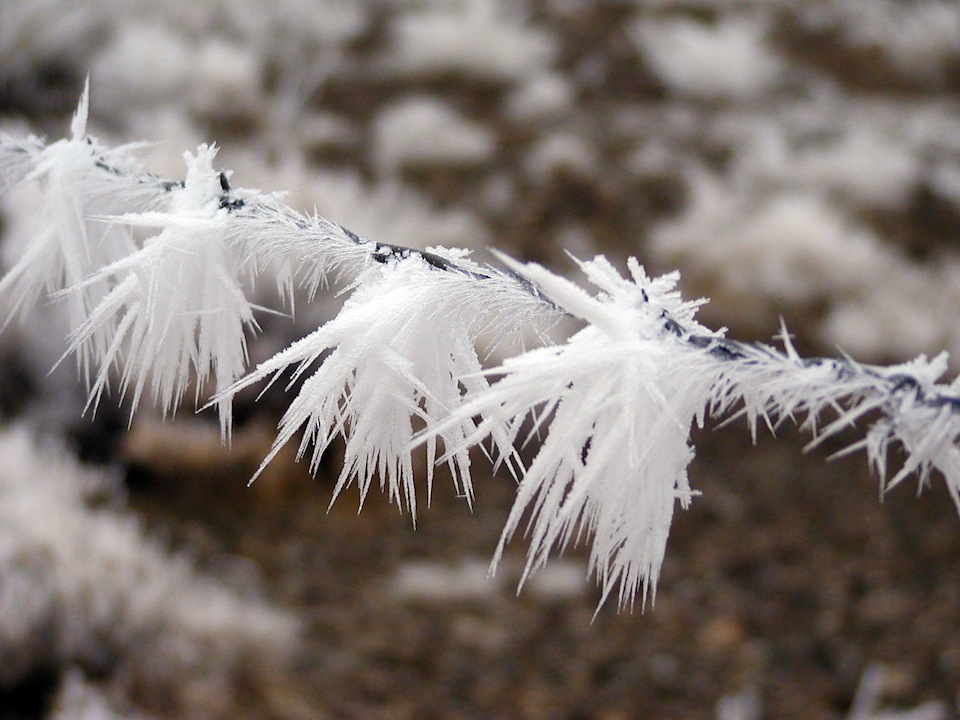
Hoarfrost: when ice crystals fall on a surface that is lower in temperature (below freezing) than the adjoining atmosphere. This state results in a rapid freezing of the moist crystals into solid state.
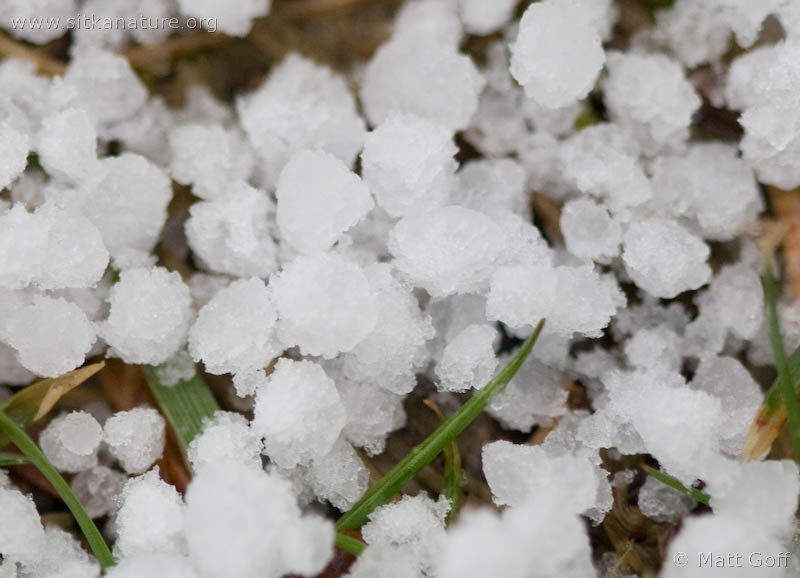
Graupel: a resultant snow type when ice crystals travel through a cloud of pure water droplets at a temperature below freezing ("supercooled cloud"). This cloud effectively rounds ice crystals, creating capsule-shaped snow.
Sleet: liquid precipitation that solidifies into snow upon deposition, creating clear spheres up to ¾ cm in diameter.
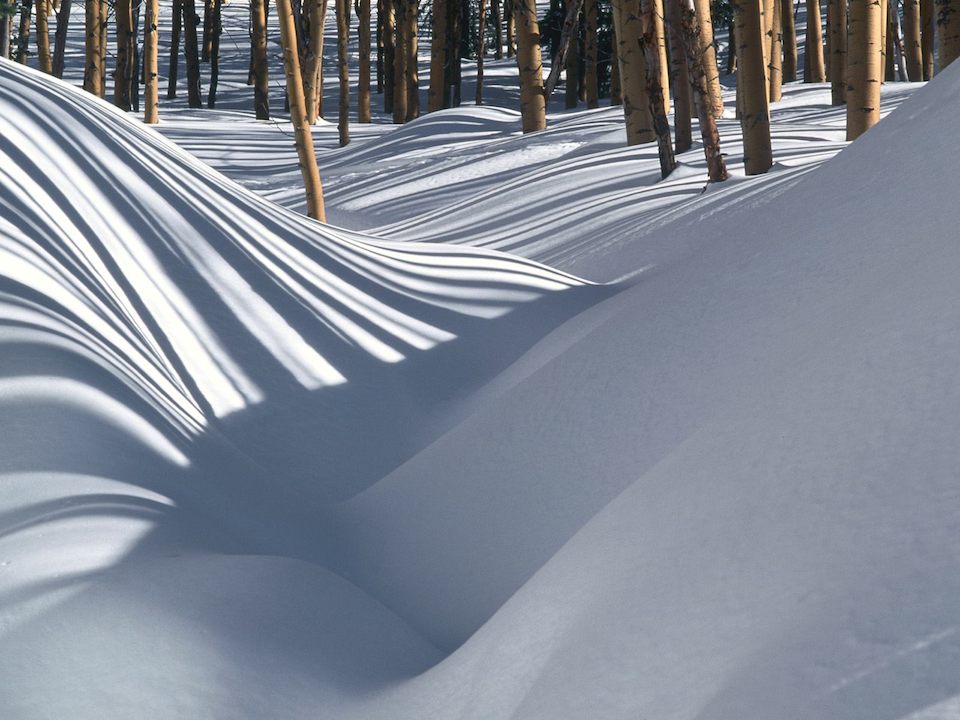
New Snow: Low density snowfall that has been newly accumulated, shapes of snow crystals are still visible.
Perennial Snow: Snowfall that deposits over numerous winter seasons, and does not thaw in melt season.
Information for definitions provided by SWIPA (2011) and NSIDC (2013).
References
Snow Links
Material on this page was provided by Maren Pauly, Department of Geography, University of Waterloo. For photograph references, hover over image.
Last updated on 02/11/2017